
Little children, do not go to Africa for a walk – or something about the social role of evil spirits and voodoo people.
Piogenic cocci, in the case of weakening the properties of the immune system of the skin (Yes, it is in the case of weakening the properties of immunity, because the normally functioning skin easily copes with numerous attacks of pyogenic microorganisms), can provoke the development of an island-inflammatory disease – pyoderma.
Obviously, before the rehabilitation, we need to know which of the cocci increased their colony - Streptococcus or Staphylococcus? To do this, you can (and should) do bakposev, but wait for its result (usually 10-14 days) is not always possible.
How to understand when viewed, what is the microorganism itself has shown? It's easy.
After being hit by pyogenic cocci in the skin (from the outside or hematogenous) and increase their number, develop nonspecific inflammation. If it is staphylococci, then exocytosis develops, in which the vessels expand, and through their walls into the surrounding tissues penetrate the leukocytes, which under the influence of leukocidin are destroyed.
The released leukotoxin affects the vascular wall, necrosis develops, and coagulase limits this process. Since all this is happening in the dermis, then our eyes open... pustule. If it is within the hair follicle, it is also follicular.
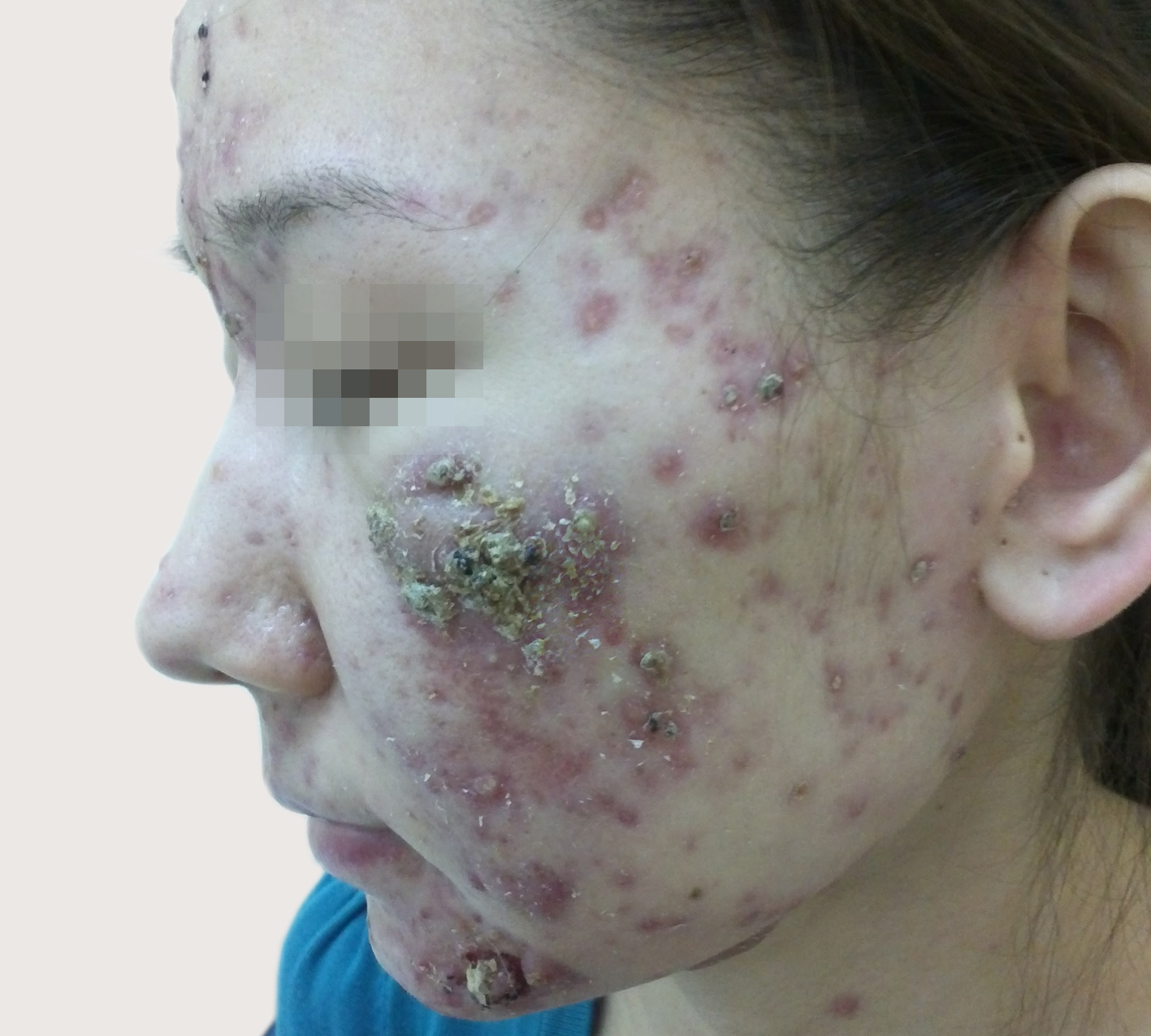
This whole picture, due to the increase in tissue volume due to infiltration and compression of free nerve endings, is accompanied by pain.
Unlike staphylococci, streptococci, when ingested in the skin in the same ways, cause the phenomenon of exoserosis, in which the degree of destruction of the walls of blood vessels is not so pronounced that the cells pass, but enough to leave the liquid part of the blood. Accordingly, edema develops and... bubble.
The process is not limited to anything, and it promotes the spread of infection in breadth and the desire for edema to the upper layers of the skin, mainly to the epidermis (less dense tissues).
Eye we see phlyctena – soft and flabby bubble filled with pus. The pain will be insignificant and only because of the feeling of tightening of the epidermis.

Now, seeing the pustule, noting the pain and infiltration – we know that Staphylococcus is hidden in the thickness of the skin, which means systemic antibiotic therapy is required, since it is easier to get into the dermis from the vascular bed, and not through the roof of the epidermal barrier.
But if we see phlyctena, it's strep, which allows us to carry out activities of local impact.
What if it's both? Especially thoughtful doctors will ask, and what if there is a mixed infection?
In this case, the first is always Streptococcus, followed by Staphylococcus. It is connected with the peculiarities of pathogenesis and speed of development of the inflammatory process in the tissues.
Accordingly, the treatment should be approached comprehensively, systematically, locally and... with the assessment and correction of immunity. Since two microorganisms can develop only in conditions of immunodeficiency in infectious type.
Good luck in clinical diagnosis, colleagues, ease in understanding the relationship of skin and microorganisms and successful treatment, and there, you see, and the results of bakposev will catch up – to test our knowledge!

Little children, do not go to Africa for a walk – or something about the social role of evil spirits and voodoo people.

Остаются считанные дни времени пребывания экспедиции Живая Параллель в Перу. Изучив тексты, увидев множество подтверждений мифов и обоснованности сведений об инках, встретившись с представителями разных социумов, возникших вследствии испанского завоевания, настало время разделить реальную жизнь с последними потомками инков. Благо, это оказалось реальностью, поскольку наш проводник Элвис, родом из народности кечуа, являющейся прямым наследником культурных традиций инков, видя нашу искреннюю (не туристическую) потребность пожить в культуре, любезно пригласил посетить его деревню.
В прошлый раз мы остановились на том, что в ответ на длительное расчесывание, кожа утолщается и это приводит к снижению порога восприятия зуда. Таким образом, возникает своеобразный «порочный круг», который объясняет трудность терапии кожного зуда, но механизм «чем больше пациент чешет, тем больше ему хочется», не единственный... читать далее
При выборе средства для ухода за кожей, покупатель предъявляет требования в первую очередь к заявленным производителем потребительским свойствам.
Оценка безопасности поставляемой в рынок продукции, без которой реализация невозможна и незаконна, охраняя здоровье потребителя, не гарантирует ему заявленную производителем эффективность. Между тем, давно существует оборудование для экспертной оценки параметров кожи, которое в руках специалистов может быть комплексно использовано для объективной оценки потребительских свойств косметической продукции.